Physical risks post the most obvious and pressing impact to supply chains, with extreme weather events clearly disrupting even the simplest global supply chain operation. Hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and heatwaves are not only becoming more frequent and severe, but also increasingly unpredictable, catching organizations unaware. Rising temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns are causing water scarcity and reducing agricultural yields, affecting the availability of common raw materials, driving up prices for businesses and consumers alike, and creating major uncertainties across industries. Furthermore, severe climate events can damage critical infrastructure such as ports, roads, and warehouses, creating long-term disruptions.
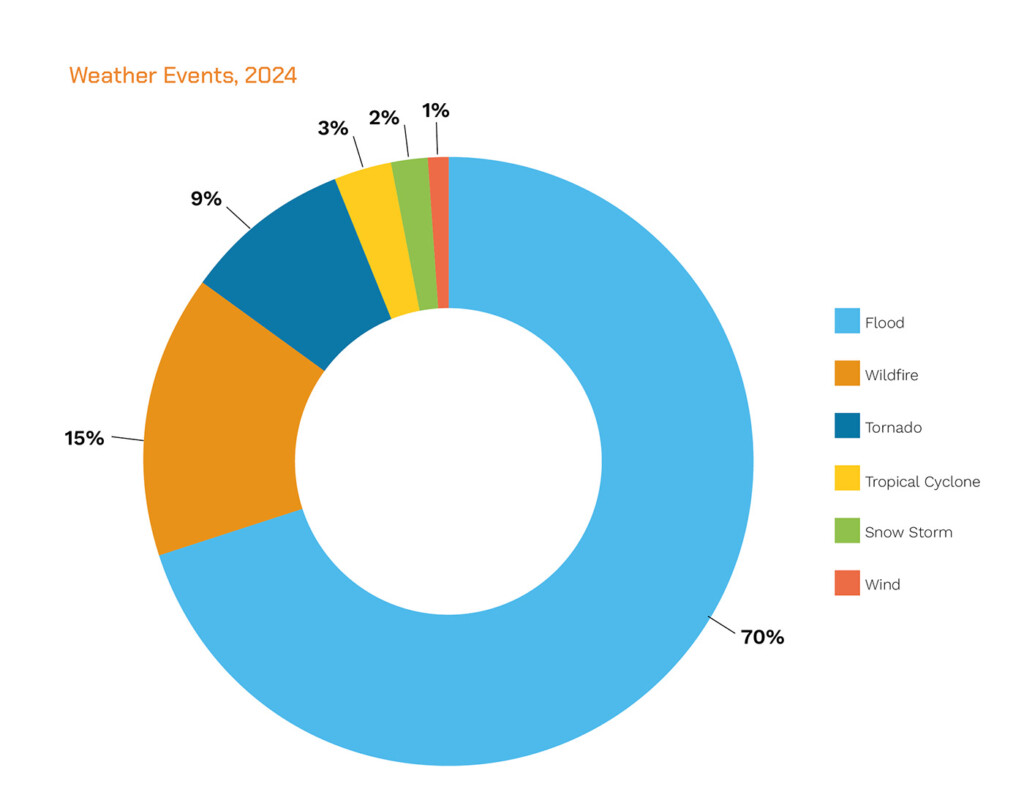 Figure 1 – Leading 2024 extreme weather events contributing to broader climate risk for 2025
Figure 1 – Leading 2024 extreme weather events contributing to broader climate risk for 2025
Past immediate needs, climate change transition risks arise from the global shift towards a low-carbon economy. Though this is a positive move overall, it requires organizations to change their processes and invest significantly into net-zero operations. Governments, regulators, and consumers are all putting pressure on businesses to move to cleaner, greener operations. Regulations promise hefty fines for companies that refuse to change their business practices. Meanwhile, consumers are demanding more sustainable products and greater transparency into sourcing practices. Companies failing to meet these expectations risk losing market share to competitors that prioritize sustainability.
Social sustainability risks
Social sustainability risks are as critical as environmental challenges in global supply chain management. Companies must actively address labor rights violations, community impacts, and the growing influence of ethical consumerism to maintain operational viability and stakeholder trust.
Exploitation in supply chains remains a pervasive issue, highlighted by recent legislations such as the US’s Uyghur Forced Labor Protection Act and Canada’s Modern Slavery Act. Practices such as child labor, forced labor, and inadequate wages are still rampant across industries such as textiles, raw material mining, and electronics manufacturing. These violations are clear human rights issues, presenting moral, regulatory and financial, and reputational risks for companies who are linked to these exploitative practices.
 Figure 2: 2024 Social Sustainability Risk by Industry: Recorded Labor Violations
Figure 2: 2024 Social Sustainability Risk by Industry: Recorded Labor Violations
Furthermore, the environmental impacts of supply chain activities can have direct consequences on local communities, whose health impacts are impacted by issues such as deforestation, water pollution, and air contamination. These issues exacerbate inequality, creating friction between businesses, regulators, and local stakeholders, and further threaten business reputation.
Finally, modern consumers are increasingly attuned to the ethical implications of their purchases. Companies are under pressure from consumers, as well as regulators, to adopt supply chain audits, adhere to international labor standards, and ensure that their operations align with ethical principles. Consumers have a great understanding of the technology at their fingertips, and expect businesses to use advanced analytics and more to ensure sustainable practices.
The bigger picture
The interconnected nature of physical climate change risks and social risks compounds supply chain vulnerabilities. For example, climate change disproportionately affects marginalized communities, exacerbating social inequalities and creating further risks. And, when supply chains are disrupted, the ripple effects are felt most acutely by those with limited means to adapt, leaving workers exposed to potentially exploitative situations.
Furthermore, increased competition for dwindling resources also heightens social tensions and exploitation, leading to conflicts between corporations and local populations. As a result, businesses may be susceptible to significant reputational and operational risks.
Therefore, businesses must balance cost-efficiency with social responsibility. While cost-cutting measures may seem financially prudent, they can come at the expense of ethical labor standards or environmentally-sound decisions. The bottom line is just one piece of the puzzle. Companies must prioritize sustainable practices, investing early to ensure balanced finances while safeguarding long-term resilience.
Next steps
A proactive and layered approach to climate and social risk mitigation is key to tackling sustainability challenges within global supply chains.
- Diversify your suppliers. First, review your suppliers, noting if your company favors only one supplier or region. Diversifying suppliers and production regions can lessen the risks of localized disruptions, ensuring business continuity during crises.
- Adopt ethical practices. Take an honest look at your business practices. Tools that use advanced technologies, such as AI-powered analytics, and that help you map your value network to the nth degree will be helpful here. Closing your eyes and hoping for the best is not an effective or acceptable strategy. Then, implement robust labor standards, conduct regular audits, and enforce compliance throughout your supply chain. If possible, engage with local stakeholders and communities as well to foster goodwill and enhance your brand reputation.
- Use technology. Technological advancements offer powerful tools to manage risks and improve transparency. Artificial intelligence and advanced analytics can efficiently sort through a variety of data sources, creating end-to-end visibility in supply chains, providing predictive modeling, and monitoring emerging risks. Investing in tools to sort through risk data will allow your supply chain management team to make the best educated decisions for your business.
- Align with global policies and regulations. Aligning with international standards ensures that companies operate within a globally recognized sustainability framework, guiding businesses to prioritize environmental and social objectives. Following the tenets of these policies early will also protect your organization from potential fines and other non-compliance risks.
Supply chains are facing escalating environmental and social challenges that demand urgent attention. By proactively addressing these risks through a layered approach, businesses can build resilient, sustainable supply chains that ensure long-term success while fostering global equity and environmental stewardship.


